Pure tungsten bar is made of 99.95% tungsten power and its forging and annealing process is shown by test. The bar has physical properties e.g. density 19.3g/cm3, melting point (liquid) 3422℃, electricity conductivity 30% IACS min and hardness 69hra min. It owns special characters including low thermal expansion, good thermal conductivity, sufficient resistance and high elastic modulus. The bar is widely applied in various fields, e.g. support line, lead-in line, printer needle, various electrodes, quartz furnace, filament, high-speed tools, automatic products, sputtering target and heating devices with special properties etc. Powder metallurgy is a popular method in production process.
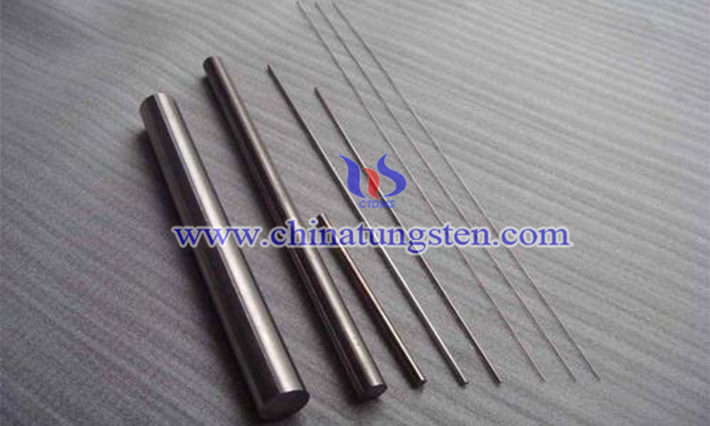

The sintered pure tungsten bar is forged and drawn by using different average forging ratio and forging method, and annealed in different annealing process. The microstructure and physical mechanical character of the samples are analyzed by metallographic microscope, hardness tester and density tester. The results are as follows:
1.0 Forging can remarkably increase the density and hardness of tungsten bar, but the tungsten bars are easy to crack provided the average forging ratio is too big, so the average forging ratio should be less than 32% when the forging temperature is below 1450℃.
2.0 Compared with the bar forged with smaller average forging ratio and one-time forging at one end, the tungsten bar forged with bigger average forging ratio and one-time forging at both ends has finer grain structure and higher hardness.
3.0 The total forging ratio is about 80%, the bar using smaller average forging ratio and one-time forging at one end can basically finish recrystallization when it is annealed at 1300℃ for 30 minutes, but if the average forging ratio is bigger and forging way it is one-time heating at both ends the tungsten bar can finish recrystallization only until the bar is annealed at 1350℃ for 60 minutes. After annealing, the hardness of tungsten bar both decreases, the hardness of first forged ways is lower than that of the second forged ways before the annealing and at the beginning stage of annealing. With the completion of recrystallization, the difference is no longer obvious.




